
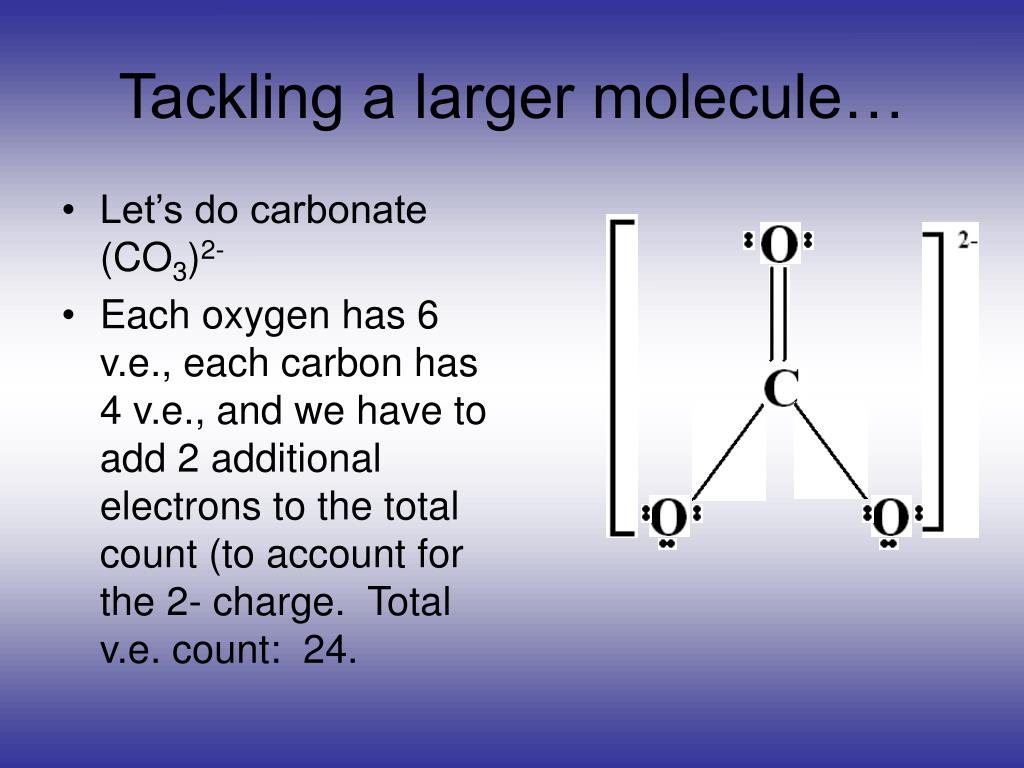
The oxidation state of any chemically bonded carbon may be assigned by adding -1 for each bond to more electropositive atom (H, Na, Ca, B) and +1 for each bond to more electronegative atom (O, Cl, N, P), and 0 for each carbon atom bonded directly to the carbon of interest.The algebraic sum of the oxidation states in an ion is equal to the charge on the ion.Īssigning oxidation numbers to organic compounds.The algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers of elements in a compound is zero.For each of the O in a single bond with carbon, formal charge 6 0.52 6 6 1 6 -1.

Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 when combined with non-metals, but it has an oxidation number of -1 when combined with metals. The formula for formal charge: Let us find out for CO32- : For Carbon, formal charge 4 0.58 0 4 4 0.Oxygen almost always has an oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides (H 2O 2) where it is -1 and in compounds with fluorine (OF 2) where it is +2.The alkaline earth metals (group II) are always assigned an oxidation number of +2.The alkali metals (group I) always have an oxidation number of +1.Fluorine in compounds is always assigned an oxidation number of -1.The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge of the ion.
#Charge of carbon in co3 free

You can find examples of usage on the Divide the redox reaction into two half-reactions page. Since the electrons between two carbon atoms are evenly spread, the R group does not change the oxidation number of the carbon atom it's attached to. Unlike radicals in organic molecules, R cannot be hydrogen. Organic compounds can be written in such a way that anything that doesn't change before the first C-C bond is replaced with the abbreviation R (Figure 1c). When dealing with organic compounds and formulas with multiple atoms of the same element, it's easier to work with molecular formulas and average oxidation numbers (Figure 1d). of the dissolved inorganic carbon is required. The formal charge of any atom in a molecule can be calculated by the following equation: Where V is the number of valence electrons of the atom in isolation (atom in ground state) N is the number of non-bonding valence electrons on this atom in the molecule and B is the total number of electrons shared in covalent bonds with other atoms in. For the essential translation of 13 of total dissolved carbon to 13 of single compounds, and conversely, the inorganic carbon chemistry, i.e. Notice that changing the CH 3 group with R does not change the oxidation number of the central atom. b) Measuring the carbon isotopic composition of a solution comes to extracting the total CO2 from the sample after acidification, instead of single compounds. R is an abbreviation for any group in which a carbon atom is attached to the rest of the molecule by a C-C bond. CO3 2 + 2NH+4 + 2H2O (Path I) (Path II) (Path III) (Path IV) (Path V) The walls of the bacterial cells had a negative charge, so cations from the.
Different ways of displaying oxidation numbers of ethanol and acetic acid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
